What is a Distributed Gap Core?
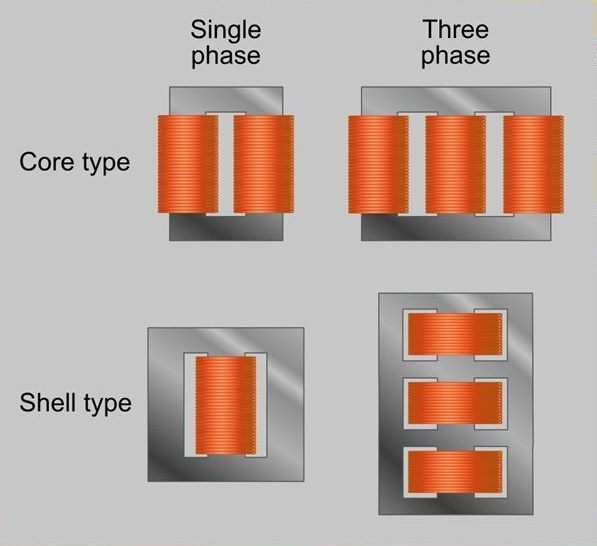
 Distributed gap wound cores, or ‘DG cores’, are amongst the most popular in the distribution transformer industry; often being found in small to medium sized transformers. They are a type of wound core that is categorized together for their single cut per lamination process. DG cores are primarily found in distribution transformers with single phase and three phase configurations which can be altered to meet specific design requirements.
Distributed gap wound cores, or ‘DG cores’, are amongst the most popular in the distribution transformer industry; often being found in small to medium sized transformers. They are a type of wound core that is categorized together for their single cut per lamination process. DG cores are primarily found in distribution transformers with single phase and three phase configurations which can be altered to meet specific design requirements.
Distributed Gap Cores offer great performance and have the advantage of utilizing a simple clamping structure and assembly process. This means they can have up to 75% fewer components as compared to an equivalent stacked core, reducing assembly time significantly. The AEM Unicore was created in 1990 as a way to reduce loss and manufacturing costs while still maintaining the advantages of the wound core. The other machine, the TRANCO, is typically a cheaper option because it is able to churn out the cores at a much higher speed.
What is a Distributed Gap Core?
 Distributed gap wound cores, or ‘DG cores’, are amongst the most popular in the distribution transformer industry; often being found in small to medium sized transformers. They are a type of wound core that is categorized together for their single cut per lamination process. DG cores are primarily found in distribution transformers with single phase and three phase configurations which can be altered to meet specific design requirements.
Distributed gap wound cores, or ‘DG cores’, are amongst the most popular in the distribution transformer industry; often being found in small to medium sized transformers. They are a type of wound core that is categorized together for their single cut per lamination process. DG cores are primarily found in distribution transformers with single phase and three phase configurations which can be altered to meet specific design requirements.
Distributed Gap Cores offer great performance and have the advantage of utilizing a simple clamping structure and assembly process. This means they can have up to 75% fewer components as compared to an equivalent stacked core, reducing assembly time significantly. The AEM Unicore was created in 1990 as a way to reduce loss and manufacturing costs while still maintaining the advantages of the wound core. The other machine, the TRANCO, is typically a cheaper option because it is able to churn out the cores at a much higher speed.

