
Like air, electricity is all around us. Today, nearly every part of the world is connected to a power grid. It is a ubiquitous part of modern society. We are so used to being around it that our brains often choose to ignore it. But have you ever stopped and wondered how this complex system generates electricity, carries it through miles of transmission lines, and delivers it to your home?
A power grid is a network of high-voltage transmission lines used to deliver electricity to consumers. To simplify this complex system, let’s break it into four small pieces: generation, transmission, distribution, and end use.
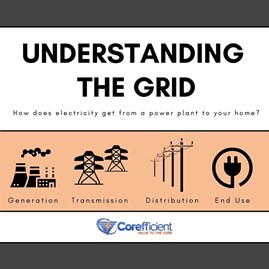
Generation
First, energy must be generated. But how? Generation of energy can come from numerous sources. The energy produced by a generator can be obtained by burning fossil fuels or creating nuclear reaction power. There are also methods of acquiring energy without harming the ecosystem, also known as green energy, in capturing wind, water, and solar energy.
Transmission and Distribution
After electricity is created from generators, the power needs to travel from the power plants to your door. This is where energy transmission and energy distribution come in. Energy from one of the previously mentioned generators then travels through the next step of its journey to a transmission substation. Here is where electrical transformers play a role. Electrical transformers convert the newly generated energy to extremely high voltages to allow the energy to travel over long distances.
This high voltage of power is then distributed to consumers. Electrical wires and poles seen along the side of a road are how the power can make the trek from generators to our homes. Wires make it possible for electricity to travel while poles provide a good return path for electrons and keep the lightning away from the wires.

End Use
Before electricity makes it to your home, it reaches another substation. In the substation, mechanisms called step-down transformers convert high voltage power to lower voltage for distribution to homes, commercial, and industrial areas. Once distributed, electricity can now be used to keep your house well lit, devices charged, and keep your food cold.
From generator to home, the entire journey of electricity is what is known as the energy grid.
Life one hundred years ago may seem distant and foreign to us today, but you may be shocked to realize that our current power grid is over 100 years old. Of course, we have made many advancements since then to meet the current energy demand and make energy distribution more efficient. Energy storage is one method that has been proven to be effective — storing surplus energy instead of wasting it. However, the most effective way to save energy is by using an efficient transformer core.

Corefficient is committed to getting the best performance out of the energy grid. We value excellence in our transformer cores, and we know that energy transmission is critical in bringing power to the consumer. We have created a new transformer core design that is more energy-efficient than ever before. Those in the industry may have some doubts about receiving a fully assembled transformer core. But we can confidently assuage all those fears as our transformer core design has undergone thorough testing at multiple stages. We can assure you that the performance of our energy-efficient cores will not suffer because of its fully assembled design.
Just as the energy grid is crucial in ensuring access to power for everyone, Corefficient is vital to energy transmission efficiency. We hope to continue to be a part of the conversation surrounding energy innovation and contribute quality products throughout North America.
More about Corefficient
Corefficient designs, manufactures, and markets energy-efficient electrical cores which are a major component used in the manufacture of dry-type and liquid-filled transformers. Based out of Monterrey, Mexico, Corefficient brings the value of people, technology, and financial strength to the transformer core market. Our goal is to ensure the consistent delivery of exceptional service, and the company looks forward to building a new legacy of value to the core.
If you would like to contact us, please visit our website or contact our North America sales engineer directly: 1 (704) 236-2510.





